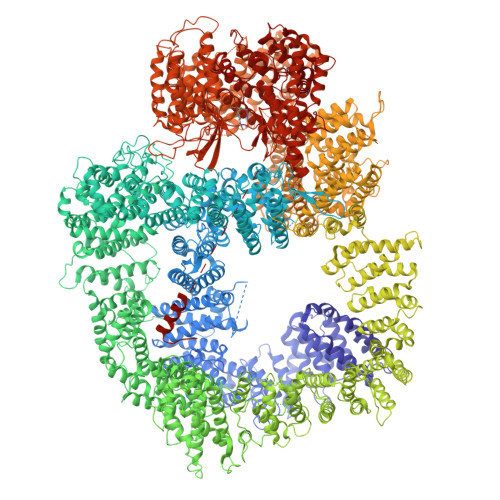
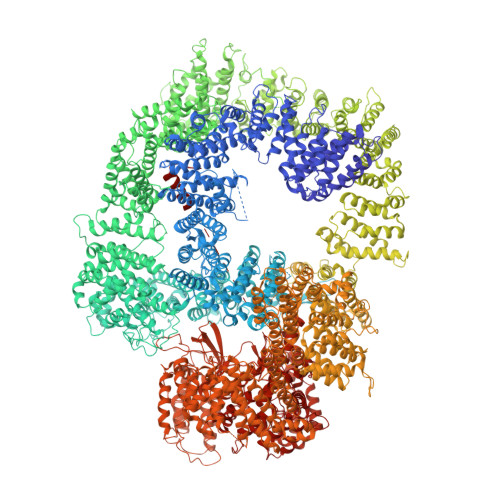
Structural insights into inhibitor regulation of the DNA repair protein DNA-PKcs.
Liang, S., Thomas, S.E., Chaplin, A.K., Hardwick, S.W., Chirgadze, D.Y., Blundell, T.L.(2022) Nature 601: 643-648
- PubMed: 34987222
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41586-021-04274-9
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
7OTM, 7OTP, 7OTV, 7OTW, 7OTY - PubMed Abstract:
The DNA-dependent protein kinase catalytic subunit (DNA-PKcs) has a central role in non-homologous end joining, one of the two main pathways that detect and repair DNA double-strand breaks (DSBs) in humans 1,2 . DNA-PKcs is of great importance in repairing pathological DSBs, making DNA-PKcs inhibitors attractive therapeutic agents for cancer in combination with DSB-inducing radiotherapy and chemotherapy 3 . Many of the selective inhibitors of DNA-PKcs that have been developed exhibit potential as treatment for various cancers 4 . Here we report cryo-electron microscopy (cryo-EM) structures of human DNA-PKcs natively purified from HeLa cell nuclear extracts, in complex with adenosine-5'-(γ-thio)-triphosphate (ATPγS) and four inhibitors (wortmannin, NU7441, AZD7648 and M3814), including drug candidates undergoing clinical trials. The structures reveal molecular details of ATP binding at the active site before catalysis and provide insights into the modes of action and specificities of the competitive inhibitors. Of note, binding of the ligands causes movement of the PIKK regulatory domain (PRD), revealing a connection between the p-loop and PRD conformations. Electrophoretic mobility shift assay and cryo-EM studies on the DNA-dependent protein kinase holoenzyme further show that ligand binding does not have a negative allosteric or inhibitory effect on assembly of the holoenzyme complex and that inhibitors function through direct competition with ATP. Overall, the structures described in this study should greatly assist future efforts in rational drug design targeting DNA-PKcs, demonstrating the potential of cryo-EM in structure-guided drug development for large and challenging targets.
Organizational Affiliation:
Department of Biochemistry, University of Cambridge, Cambridge, UK. sl744@cam.ac.uk.